Marijuana anatomy is not just a set of structures and organs, it is the key to successful growing and obtaining maximum yields from the plant. Each part of the plant performs its unique role.
The anatomy of the marijuana plant is also closely related to cultural and historical significance. This plant serves not only as a source of pleasure, but also as an important component in medical and industrial fields. Studying its structure helps to better understand what components make it so unique and in demand in various industries.
Basic anatomical elements
Let's get acquainted with the main anatomical elements of marijuana plants:
- Root system: This is the starting point where the plant absorbs water and minerals from the soil. Marijuana's root system has an amazing ability to extract essential nutrients, creating a strong foundation for healthy growth.
- Stem: The main stem of a plant that supports its vertical position. The importance of the stem in the structure of marijuana lies not only in its mechanical function, but also in the transportation of water and nutrients throughout the plant.
- Marijuana fan leaves are large, fan-shaped structures that are a key element of the plant. These leaves play an important role in the process of photosynthesis, converting sunlight into the energy necessary for the growth and development of cannabis. Its shape and size can also serve as indicators of the plant's overall health, and its strong veins can contain important biochemically active substances, making it valuable for the production of extracts.
- Marijuana sugar leaves are young, covered with beautiful trichome crystals, leaves that are usually cut off before drying. Their excellent coverage of cannabinoids and terpenes makes sugarcane leaves a valuable raw material for creating high-quality oils, extracts and other cannabis products.
- The cola of marijuana is the upper, most valuable part of the bush, consisting of densely collected flowers. This central "cone" structure is the site of the highest concentration of cannabinoids and terpenes, which give the plant its unique properties. Cola is rich in trichome crystals and its development is carefully monitored during the growing process.
- Marijuana calyxes are small structures located at the corners where the leaves join the stem. They play a key role in the formation of future flowers, as buds develop from them. Calyxes covered with trichomes contain numerous terpenes and cannabinoids, contributing to the overall chemical composition of the plant. Tracking calyx development is important to determine potential yield.
- Marijuana stigma is a hair-like outgrowth, usually white, located on the surface of female flowers. These hairs are pollen receiving organs and play a key role in the pollination process. However, in female marijuana plants, stigmas often serve as an indicator of bud maturity. When the stigmas change color from white to orange, this may indicate readiness for harvesting.
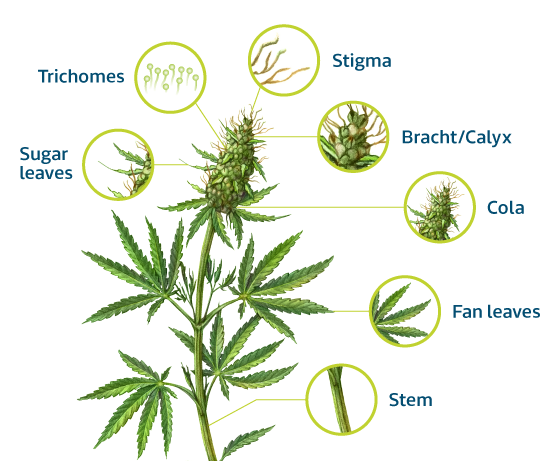
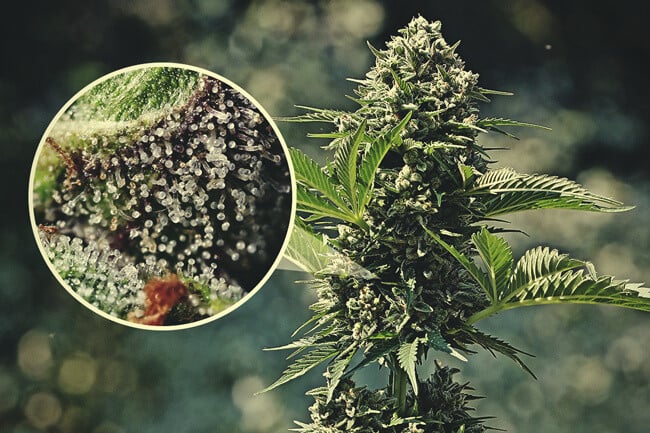
The role of trichomes in marijuana
Trichomes are microscopic hair-like growths that cover the surface of a plant, including leaves, stems, and even buds. They are a real source for biochemically active substances such as cannabinoids and terpenes.
- Different types of trichomes: There are several types of trichomes, each with its own unique function. The main ones are club-shaped trichomes, which contain high concentrations of cannabinoids, and smooth trichomes, which produce aromatic terpenes. This complex interaction makes trichomes key players in shaping the characteristic properties of each marijuana strain.
- Functions of trichomes: The main function of trichomes is to protect the plant from pests and UV radiation, but for cannabis connoisseurs, their ability to produce unique chemical compounds makes them especially valuable. Cannabinoids such as THC and CBD, as well as the terpenes that give marijuana its smell and taste, are produced in the trichomes.
- How trichomes affect marijuana quality: The density and condition of trichomes directly affect the quality of the crop. Plants with abundant trichomes usually have a higher content of cannabinoids and terpenes, which in turn gives the crop brighter effects and a richer taste.

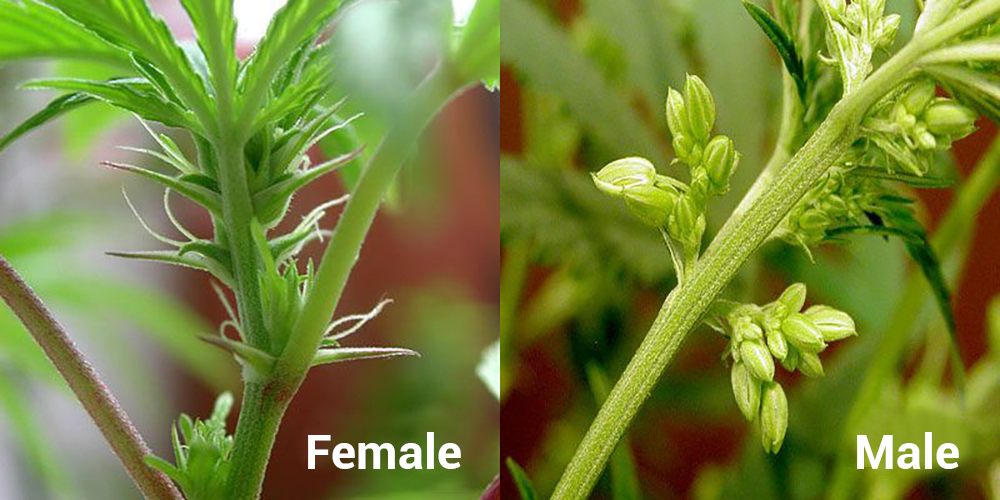
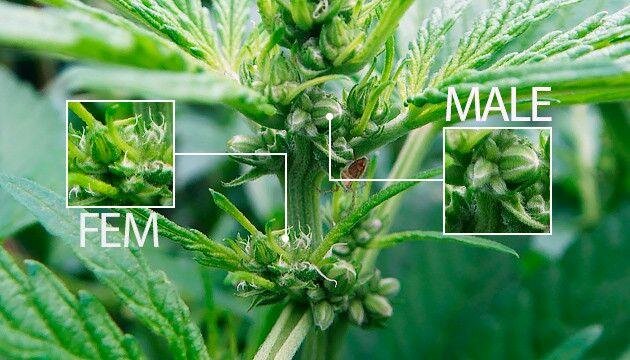
Differences between male and female plants
In the world of marijuana, the differences between male and female plants are a key aspect of successful growing. Let's look at how these differences affect the plant and why understanding the sex of the plant is so important.
You can determine the sex of the plant by paying attention to its flowering. Female plants develop buds containing high concentrations of cannabinoids, while male plants produce pollen. Moreover, male plants are usually less desirable for growing, since their flowering does not bear fruit in the form of buds.
Female plants that produce flowers are what many growers strive for. Their buds contain high levels of THC and CBD, making the plant suitable for medicinal or recreational purposes. Choosing female plants also ensures a higher yield because each bud can become a potential crop.
Male plants, in turn, play an important role in the pollination process. However, if the goal is to obtain a high-quality crop, male plants are usually removed to prevent fertilization of female flowers, which can reduce the quality of the crop.
Hermaphrodites - sometimes plants can become hermaphrodites, having both female and male organs. This can happen due to stress or genetic factors. Hermaphrodites can also lead to fertilization and reduced crop quality.

Hermaphrodites
Hermaphrodites are plants that have both male and female characteristics. Although nature can sometimes create hermaphroditism as a survival mechanism, in the world of cannabis, hermaphroditism is often considered an undesirable factor. Let's consider why hermaphrodites appear, how this can affect the harvest, and how to prevent their formation.
- Causes of hermaphroditism: plants can become hermaphrodites due to stressful conditions, such as sudden changes in lighting, temperature changes, overloading with fertilizers or other factors. Genetics can also play a role, especially if the seeds come from plants with a predisposition to hermaphroditism.
- The effect of hermaphroditism on the crop: hermaphrodites can create pollen that fertilizes female flowers. This can lead to the development of seeds in the buds, which is undesirable for most growers, since the seeds can deteriorate the quality of the final crop.
- Prevention of hermaphroditism: one of the ways to prevent hermaphroditism is to create stable conditions for the plant. This includes regular lighting, moderate fertilization, temperature and humidity control.
- Detection of hermaphrodites: regular monitoring of plants will help detect hermaphrodites at an early stage.
Understanding the causes, effects and methods of preventing hermaphroditism will help the grower to ensure a stable and high-quality harvest.











Write a comment