The future of cannabis cultivation is already here it's environmentally friendly, efficient, and sustainable. This is all thanks to aquaponics a system combining fish farming (aquaculture) and hydroponics (growing plants without soil). More and more home growers and commercial cultivators are choosing this method. Why? In this article, we'll explore this method and briefly describe its processes and interactions.
What is aquaponics and how does it work?
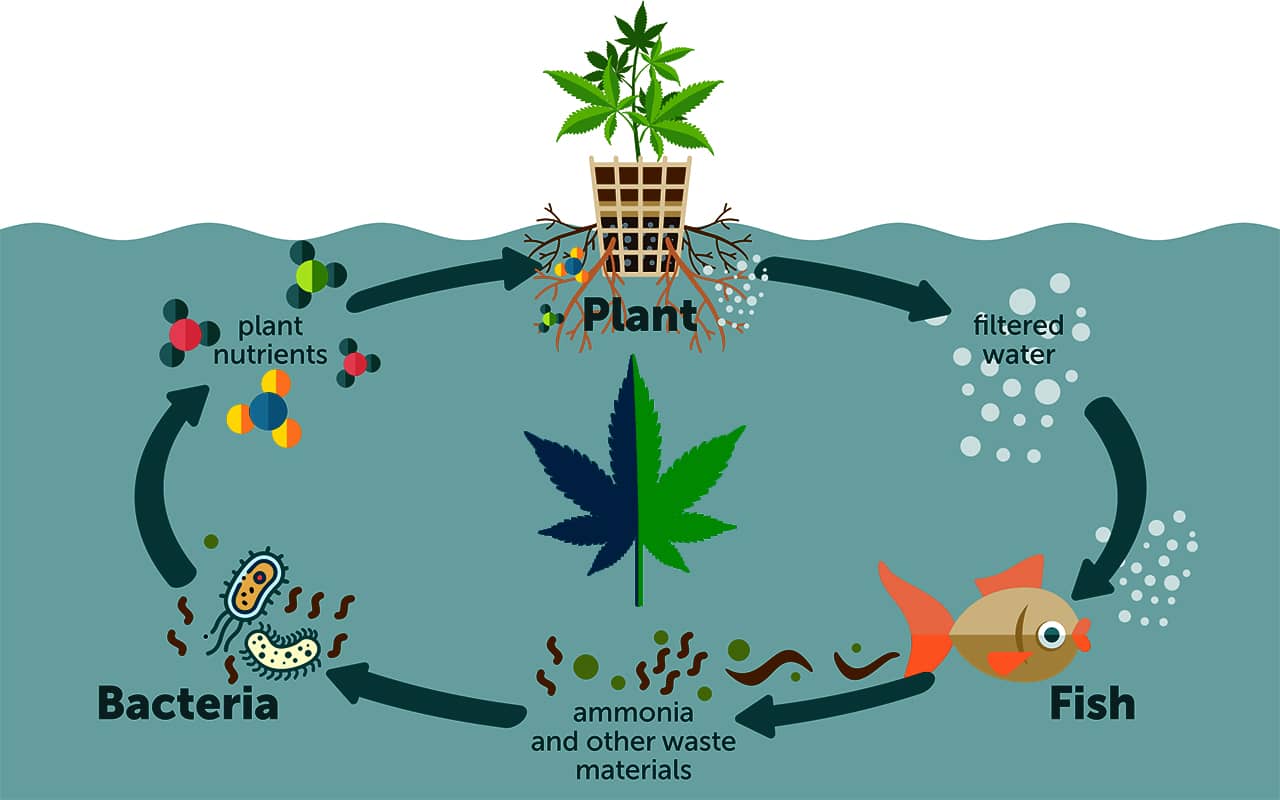
Aquaponics is a closed-loop ecosystem in which fish waste serves as nutrients for plants, while the plants clean the water, returning it to the fish. The process is as follows:
- Fish produce waste → water becomes nutrient rich.
- Beneficial bacteria convert waste into nutrients available for plants.
- Cannabis absorbs the nutrients → clean water returns to the fish.
This way, the system functions without chemical fertilizers, minimizes water consumption, and maintains an organic cycle.
Why Aquaponics is ideal for cannabis

Aquaponics uses up to 90% less water compared to traditional soil cultivation methods, making it ideal for dry regions and eco-conscious growers. Plants receive natural nutrients from fish waste without synthetic additives and chemicals.
Thanks to the rich organic composition of nutrients, cannabis often becomes more aromatic, terpene-rich, and potent. Constant access to oxygenated water and fresh nutrients accelerates plant growth and increases yields.
How to set up an Aquaponics system
Selecting fish
Suitable species:
- Tilapia — hardy, fast-growing, and tolerant of temperature changes.
- Koi Carp — low-maintenance, produce nutrient-rich waste.
- Catfish — adaptable to various water conditions.
Tip: Avoid fish requiring highly acidic or alkaline pH levels; cannabis prefers a pH range of 5.5–6.5.
Main system components

- Fish Tank — approximately 40 liters (10 gallons) per plant.
- Grow Bed — area where cannabis plants grow.
- Filtration System — converts waste into nutrients.
- Pump and Aeration — ensures oxygen delivery and water circulation.
Maintaining balance
- pH Levels — maintain between 5.5–6.5.
- Nutrient Levels — monitor nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
If signs of deficiency appear, supplement with organic additives such as seaweed extract.
Common issues and their solutions
- Algae Growth — reduce light exposure on the water surface, improve filtration.
- pH Fluctuations — test weekly, adjust with natural buffers (crushed coral, citric acid).
- Root Rot — ensure adequate aeration, avoid overcrowding the grow bed.
- Fish Health Problems — avoid overfeeding, regularly check ammonia and nitrate levels.
This cultivation method is not just a trend—it’s a conscious choice for sustainable agriculture. It helps reduce water usage, eliminates chemicals, and produces high-quality organic products. Increasingly, growers are adopting aquaponics to cut costs, increase yields, and meet ecological standards.
Conclusion
Growing cannabis seeds with aquaponics is not only environmentally friendly but also cost-effective. The system suits both beginners and experienced cultivators, ensuring rapid growth, potent buds, and a clean conscience—without harming the environment.
Warning! Errors Seeds does not encourage or assist you in growing cannabis. Cultivation is prohibited by the legislation of Ukraine. The article is of scientific and introductory interest only.









Write a comment