Content
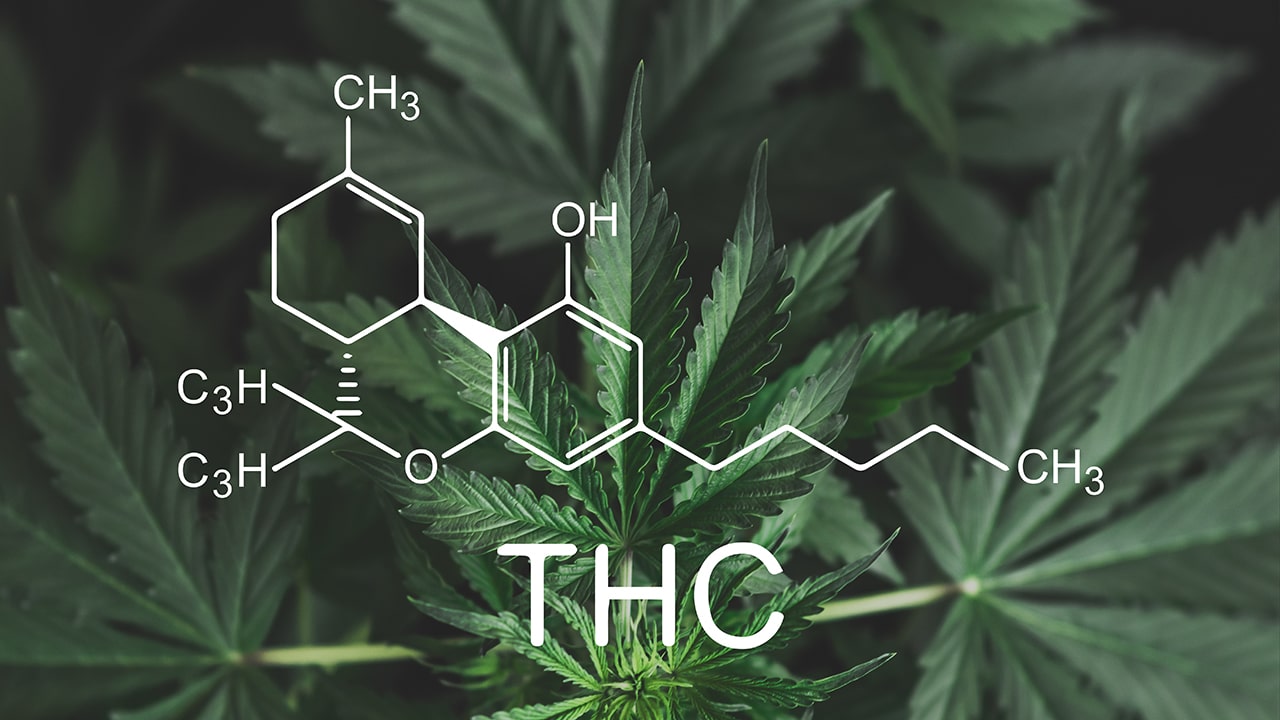

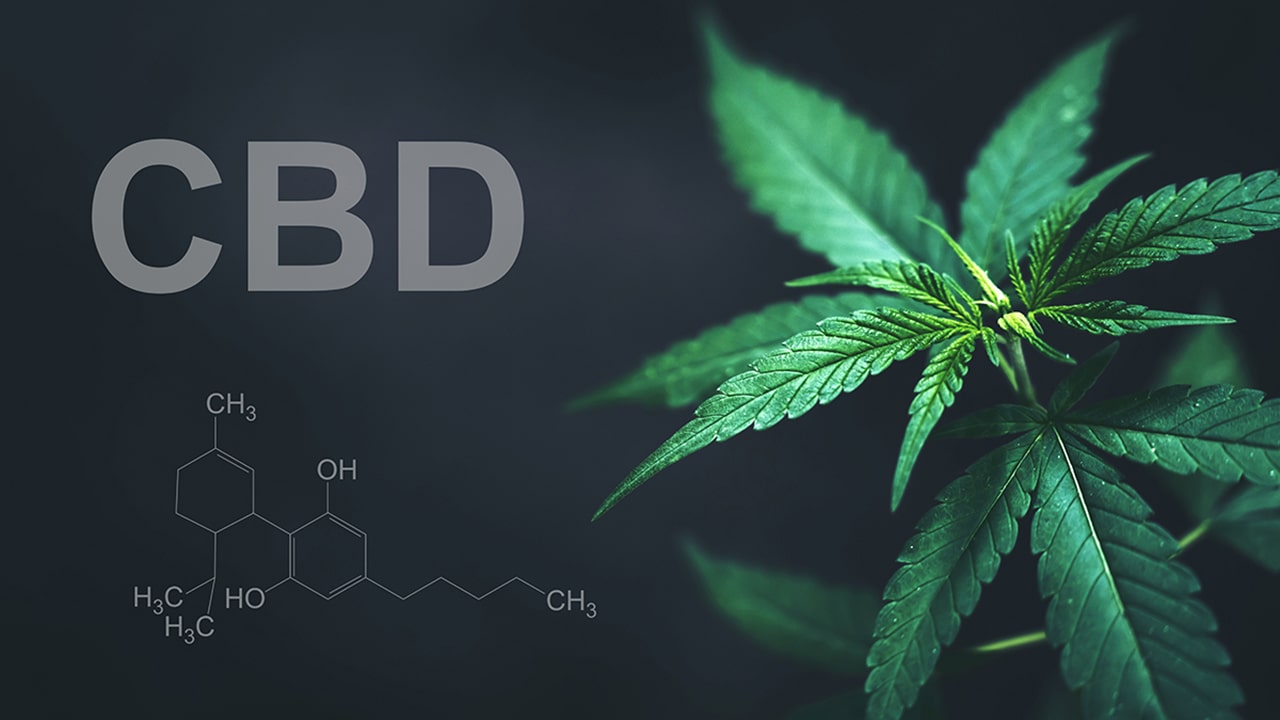
Cannabis, also known as marijuana, is a plant widely used for both medicinal and recreational purposes. Cannabis contains many active compounds known as cannabinoids, the main ones being tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Depending on the content of these substances, cannabis is divided into two main types, indica and sativa, each with different effects on the brain and the body as a whole.

Indica effect on the brain
Indica is one of the two main subspecies of cannabis, which is characterized by its unique characteristics and effects on the body. Indica varieties of cannabis usually originate from regions with colder climates, such as the Himalayas and Afghanistan. These plants have distinctive broad leaves and grow more compactly compared to sativa. Indica traditionally has a higher THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) content and a relatively low CBD (cannabidiol) content, which determines its strong psychoactive properties.
Physiological effects of indica on the brain
The main psychoactive component of cannabis is THC, which affects the central nervous system by interacting with cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors located in the brain and throughout the body. When indica is consumed, THC quickly penetrates the blood-brain barrier where it binds to CB1 receptors. This interaction causes changes in the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, resulting in the characteristic effects of relaxation and euphoria.
The high THC content of indica contributes to a stronger sedative effect. Grovers often describe the state after indica use as “heavy” or “sleepy”, due to its ability to reduce activity in the cerebral cortex and limbic system, which is responsible for emotional reactions and memory formation.
Cognitive impact and potential risks
Indica's effects on the brain include an enhanced sense of relaxation, peacefulness, and sometimes drowsiness. This is due to the suppression of neural activity, which can be beneficial for people suffering from insomnia or chronic pain. In addition, due to its ability to reduce activity in the amygdala (the area of the brain responsible for fear and anxiety), indica can be useful in managing states of anxiety and stress.

Sativa effect on the brain
Sativa is the second main subspecies of cannabis and is characterized by its unique properties and effects on the body. Sativa-type cannabis varieties typically originate from warm climate regions such as Central and South America, Africa, and Southeast Asia. These plants are characterized by narrow leaves and tall stature, which is different from the more compact indica. Sativa typically contains less THC than indica and more CBD, which is what determines its stimulating and invigorating effects on the brain.
The physiological effects of sativa on the brain
The main effects of sativa on the brain are related to its stimulant properties, which are due to the combination of various cannabinoids and terpenes. When sativa is consumed, cannabinoids such as THC interact with CB1 receptors in the brain, particularly in areas associated with the regulation of mood, attention and perception.
THC stimulates the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in feelings of pleasure, motivation, and attention. This results in an enhanced sense of euphoria and mood elevation, making sativa popular for use during the daytime when you need to stay active and alert. It is also noted that sativa can enhance creative thinking and feelings of inspiration, making it popular among artists, musicians, and other creative people.
Cognitive impact and possible side effects
On a cognitive level, sativa is often associated with increased attention and focus. Sativa users may experience an improved ability to focus on tasks and increased perception of the environment. These effects are associated with the activation of the prefrontal cortex, the area responsible for complex thinking, planning, and decision-making.
However, despite the positive cognitive effects, sativa use can also be accompanied by negative side effects. In particular, high doses of THC can cause feelings of anxiety, paranoia, and even panic attacks in some users, especially those who are predisposed to anxiety disorders. This is because THC can increase activity in the amygdala, the area of the brain responsible for processing fear and anxiety.
In addition, excessive sativa use can lead to cognitive impairments such as memory problems, impaired concentration, and slower reactions. These effects are especially noticeable in people who use sativa in large amounts or on a regular basis, as the brain adapts to constant exposure to THC, which can lead to cognitive decline.

WARNING! Errors Seeds does not encourage or encourage you to grow cannabis. Cultivation is prohibited by the legislation of Ukraine. The article is only of scientific and educational interest.










Write a comment