Content
- How multiple propagation of a single variety changes its characteristics
- Why are genetics degenerating and how to avoid it?
- Methods to prevent degradation of genetics
How multiple propagation of a single variety changes its characteristics
Any cannabis strain retains its identity only if breeding principles are strictly adhered to. However, significant changes can occur during its long-term propagation without proper control.
Mutations and natural evolution
Each generation of plants undergoes small random mutations. In nature, these mutations play an important role in helping species adapt to new conditions, but in breeding cannabis they can be undesirable.
For example, if the original variety had dense, resinous buds and a distinct fruity aroma, after a few generations, without proper control, some plants may develop less dense inflorescences, altered aroma or even reduced THC content.
Genetic recombination
When pollination occurs, the genes of the parent plants mix to create new combinations. Even if two plants of the same variety are used, their offspring may differ slightly from the original genetic code.
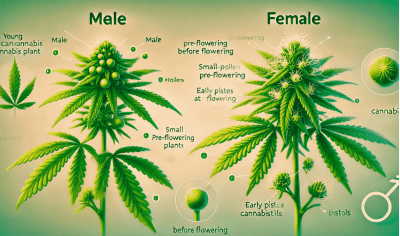
This is particularly noticeable when breeding feminized and autoflowering varieties: if the breeder is not strictly selective, the variety may gradually lose its key characteristics and individual phenotypes may differ significantly from each other.
Environmental influences
Even within the same cultivar, plants grown under different conditions may show different traits. For example, cannabis cultivated in the open can adapt to the climate by changing its growth rate, height and inflorescence density. Over time, these changes may become fixed in genetics if marijuana seeds are derived from plants grown under such conditions.
Mistakes in breeding
When a variety is repeatedly propagated, errors can occur that lead to variation in the variety. The main reasons for this are:
- Lack of control over genetic purity. If cross-pollination with another variety is accidentally allowed, undesirable gene mixing can occur.
- Use of unstable parent plants. If a breeder chooses seeds without carefully checking their characteristics, the variety may lose its predictability over time.
- Inbreeding. Overuse of the same genetic material can result in weak and non-viable plants.

Why are genetics degenerating and how to avoid it?
Genetic degradation is the gradual deterioration of a plant's characteristics, resulting in lower yields, weakened immunity and altered flavor profile. This process can occur for a number of reasons, and if not addressed in time, the variety will lose its key characteristics over time.
Inbreeding (close inbreeding)
If the same variety is propagated within a limited population without updating the genetic material, it leads to the accumulation of harmful mutations. As a result, plants become less viable and may be less able to withstand disease and stress conditions.
Signs of inbreeding:
- Slow plant growth.
- Low yields.
- Weakened immunity to fungi and pests.
- Less variation in phenotypes (all plants become similar but with weakened characteristics).
Cross-pollination with undesirable plants
If cannabis is grown in the open or in greenhouses without proper isolation, pollen from random plants can reach the female plants and lead to altered genetics. This is especially critical when breeding feminized and autoflowering varieties.
Consequences of uncontrolled cross-pollination:
- Loss of unique traits of the variety.
- Emergence of unstable phenotypes.
- Decrease in THC and CBD levels.
Mistakes in seed selection
Even if a variety is stable, its degradation can occur due to poor seed selection for further multiplication. If a breeder selects seeds based on external traits alone, ignoring their genetics, the variety gradually loses its unique characteristics.
- Using seeds from weak or diseased plants.
- Selecting random seeds without testing their progeny.
- Multiplication of seeds from unstable hybrids.
Influence of stress factors
Plant genetics can be altered by unfavorable environmental conditions. If plants are subjected to severe stress (temperature fluctuations, nutrient deficiencies, drought or overwatering), this can lead to changes at the genetic level.
Main stressors:
- Abrupt temperature fluctuations.
- Lack or excess of fertilizers.
- Change of lighting regime.
- Damage caused by insects or diseases.

Methods to prevent degradation of genetics
To keep a variety in its original form and avoid deterioration, breeders employ several key strategies:
Genetic renewal (outcrossing)
Outcrossing is crossing with related but genetically stable material. This helps to “refresh” the variety, strengthen its immunity and maintain its main characteristics.
Example: If a variety shows signs of inbreeding over several generations, it can be crossed with the same variety but from a different genetic lineage.
Cloning the best phenotypes
One of the most effective ways to preserve genetics is to clone strong plants. Propagation through clones avoids the changes associated with genetic drift.
Benefits of cloning:
- Complete identity to the parent plant.
- No random genetic mutations.
- Possibility to grow stable batches of plants.
Strict seed selection
To avoid accumulation of undesirable traits, breeders make careful selection of seeds before further multiplication.
Selection methods:
- Growing a test batch of seeds and observing their phenotypes.
- Eliminating weak and unstable plants.
- Use of laboratory tests to verify genetic purity.
Control of growing conditions
Minimizing stresses helps plants develop without mutations and changes in genetics. Optimal conditions include:
- A stable temperature regime.
- Sufficient amount of light.
- Proper nutrition (micro- and macronutrients).
- Protection from pests and diseases.
Conclusion
Genetic degradation is a serious problem that can lead to the loss of the unique properties of a cannabis variety. However, it can be prevented through proper breeding, regular updating of genetic material and strict control of grovelling conditions.

Attention! Errors Seeds does not encourage you to grow cannabis and does not promote it in any way. Cultivation is prohibited by the legislation of Ukraine. The article is of scientific and introductory interest only.








Write a comment