Content
General properties
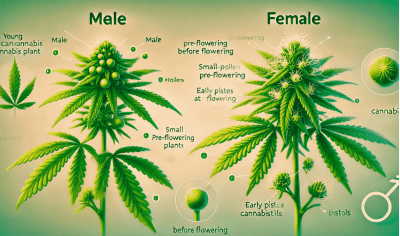
Hemp pollen is the tiny particles produced by male plants to pollinate female plants. It is a key element for plant reproduction in nature. However, its ability to spread over long distances makes it a problem for cultivators, especially when growing feminised cannabis seeds, where it is important to avoid accidental pollination.
Physical characteristics of pollen
Hemp pollen is extremely lightweight, which allows it to easily rise into the air and be transported over significant distances. Each particle is microscopic in size, making it almost invisible to the eye. It remains viable for several days, especially when humidity is low.
Factors affecting propagation range
Hemp pollen is anemophilic, meaning it is spread primarily by the wind. The wind can carry it up to several kilometers. In light winds (up to 5 km/h), pollen spreads hundreds of meters. In strong wind gusts (more than 15 km/h), its range increases significantly, reaching several kilometers.
Depending on the landscape, the distance of pollen dispersal may vary. In flat areas, pollen flies longer because there are no obstacles. In mountainous areas or dense vegetation, its movement slows down and particles settle faster.
In dry and warm weather, pollen remains light and volatile, which increases its spreading range. Humid air causes pollen particles to absorb moisture, making them heavier and settling closer to the source.

Maximum propagation distances
Hemp pollen has the unique ability to travel long distances due to its lightness and wind-borne ability. This property is extremely important to nature, as it ensures that plants can be pollinated even when they are far away from each other.
How far pollen can spread?
The maximum distance that cannabis pollen can spread depends on many factors:
- Average: under natural conditions, pollen can spread over distances ranging from a few hundred meters to 2-3 kilometers.
- In extreme conditions: studies show that pollen can travel up to 10 kilometers in strong winds and in the absence of physical barriers.
In flat areas where there are no wind obstacles, pollen from male plants can reach neighboring farms, causing cross-pollination. This is especially critical for growers of pure sativa or indica lines.
In mountainous areas, pollen rarely travels long distances due to the topography. Here the particles settle faster as the air loses its mobility as it rises.
In urban areas, pollen is usually spread over short distances due to the presence of many obstacles such as buildings, fences and trees.

How plants are protected from pollen
One of the most effective methods is the use of physical barriers. For example, fine mesh nets or special protective films can significantly reduce the likelihood of pollen entering the plantation. These barriers are especially useful for open areas where the likelihood of wind exposure is high. Living barriers of dense shrubs or trees are also planted around the plantation. These natural barriers reduce the force of the wind and trap pollen, preventing it from reaching the female plants.
Timely removal of male plants is also an important step. Regular inspection allows male specimens to be identified in time and removed before pollen release begins. If both male and female plants are grown, they should be placed far away from each other to reduce the chance of pollination.
The use of controlled conditions, such as ventilation with air filtration, is an additional protective measure. In growboxes and greenhouses, experienced growers recommend installing filtration systems that clean the incoming air of pollen and other particles. This is especially important during periods of mass pollen release, when plants are most vulnerable.
Effectively protecting plants from pollen requires a comprehensive approach. By incorporating physical barriers, proper planting placement and the use of modern technology, the risks of cross-pollination can be significantly reduced and crop quality maintained.

Warning! Errors Seeds does not encourage you to grow cannabis and does not promote it in any way. Cultivation is prohibited by the legislation of Ukraine. The article is of scientific and introductory interest only.








Write a comment