Content
- Gas chromatography (GC)
- High resolution liquid chromatography (HPLC)
- Thin layer chromatography (TLC)
- Measurement features in different types of cannabis varieties
Measuring the THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) content of cannabis is an important process for determining its psychoactive and medicinal properties. There are several techniques that are used to accurately determine the concentrations of these cannabinoids in the plant.
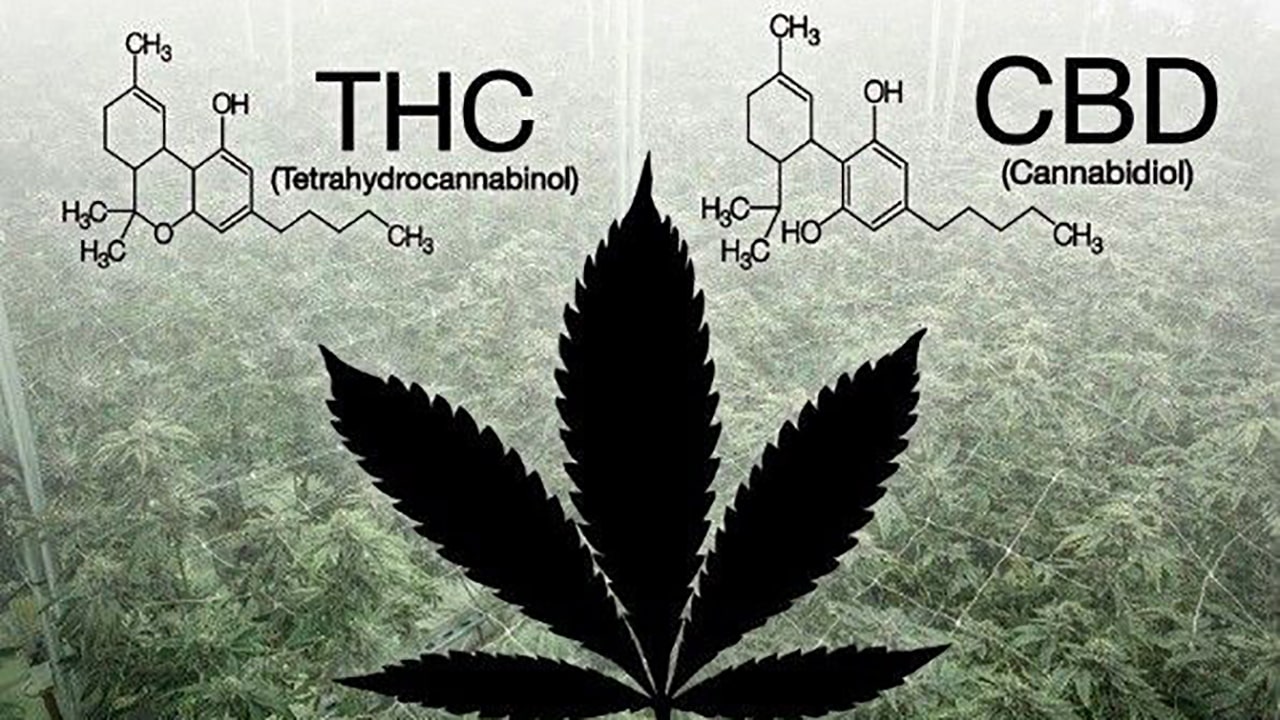
Gas chromatography (GC)
Gas chromatography is one of the most common methods for analyzing the THC and CBD content of cannabis. This method is based on the separation of the components of the mixture by vaporizing them and passing them through a column filled with a special sorbent.
- Sample preparation: first, a sample of cannabis, whether sativa or indica, is dried and pulverized. The cannabinoids are then extracted by dissolving them in an organic solvent.
- The process of analysis: the extract is introduced into a gas chromatography apparatus where it is heated to high temperatures. Under the influence of the heat, the cannabinoids vaporize and pass through a column filled with a sorbent that traps different components of the mixture for different lengths of time.
- Identification and quantification: when the components reach the end of the column, they are detected by a detector that measures their quantity. The results are displayed as a chromatogram, a graph where each substance is represented by a peak. The area of the peaks is proportional to the concentration of the substances in the sample.
Gas chromatography is suitable for the analysis of various types of cannabis, including feminized and autoflowering varieties, but it requires thermal decarboxylation, which may affect the stability of some cannabinoids.
High resolution liquid chromatography (HPLC)
High-resolution liquid chromatography (HPLC) is another widely used method for the analysis of THC and CBD in cannabis. Unlike gas chromatography, HPLC does not require heating of the sample to high temperatures, thus preserving the chemical structure of the cannabinoids.
- Sample preparation: Similar to the gas chromatography method, the cannabis sample is first dried and pulverized. The cannabinoids are then extracted using a suitable solvent.
- The analysis process: the resulting extract is introduced into an HPLC column, where it passes through a liquid sorbent under pressure. The components of the mixture interact with the sorbent and are separated according to their chemical properties.
- Identification and quantification: as the components exit the column, they are captured by detectors such as ultraviolet (UV) or mass spectrometry detectors. The data obtained is displayed as a chromatogram, where each peak represents a different cannabinoid. The area of the peaks allows the concentration of THC and CBD in the sample to be determined.
This method is the preferred method for the analysis of feminized and autoflowering cannabis varieties, as it allows accurate measurement of not only THC and CBD, but also their acidic forms, THCA and CBDA, without thermal decomposition.
Thin layer chromatography (TLC)
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) is a simpler and less costly method of analysis that is used to quickly identify cannabinoids in a sample.
- Sample preparation: similar to other methods, the sample is dried, pulverized and extracted using a solvent.
- Analysis process: the extract is applied to a thin layer of adsorbent (e.g. silica gel), which is applied to a plate. The plate is placed in a chamber with solvent and the components of the extract move across the adsorbent at different rates depending on their chemical properties.
- Identification and semi-quantitative analysis: as the components move across the plate, spots are formed that can be visualized using UV light or special reagents. The size and intensity of the spots allow the presence and approximate concentration of THC and CBD in the sample to be inferred.
Although TLC is less accurate than GC and HPLC, this method can be useful for rapid analysis of cannabis in the field or small laboratories.

Measurement features in different types of cannabis varieties
The percentage of THC and CBD in cannabis varies considerably depending on the type of variety. The main types of cannabis varieties include sativa, indica, hybrids, autoflowering and feminized varieties. Each of these types has unique characteristics that affect cannabinoid content.
Sativa
Sativas are generally known for their stimulating effects and high THC content. These varieties are often used during the daytime to boost energy and improve mood. The CBD content of sativas is usually lower compared to indica.
- Percentage cannabinoid content: sativas can contain between 15% and 30% THC, depending on genetics and grooving conditions. CBD levels in sativas are usually lower, often less than 1%.
- Measurement methods: High-resolution liquid chromatography (HPLC) is often used to accurately measure THC and CBD in sativas, as it can determine not only the THC content, but also its acid form (THCA), which has no psychoactive properties but converts to active THC when heated.
- Influence of growing conditions: in sativas, cannabinoid content can vary significantly depending on cultivation conditions, including light, moisture levels and plant nutrition. Thus, it is important to take these factors into account when measuring cannabinoids in sativas.
Indica
Indica varieties of cannabis tend to contain higher levels of CBD and have more relaxing and sedative effects. Indica is often used for nighttime use or to relieve pain and stress.
- Percentage of cannabinoid content: Indica varieties can have THC levels between 10% and 20%, although varieties with higher THC content are also found. The CBD in indica is often between 0.5% and 2%, and in some cases much higher.
- Measurement methods: for indica, as for sativa, HPLC is the preferred method, especially if both THC and CBD levels are to be measured. This is important for varieties that are used for medicinal purposes, as such varieties may have a balanced content of both cannabinoids.
Differences in CBD content: unlike sativas, the CBD content of indica can be more pronounced, making these varieties popular for medicinal purposes where the anti-inflammatory and anti-anxiety properties of CBD are important.
Hybrids
Hybrids are a combination of sativa and indica, and their cannabinoid profile can vary widely depending on the ratio of sativa and indica genes.
- Percentage cannabinoid content: hybrids may have different levels of THC and CBD depending on the parental varieties. Hybrids can be either high in THC or balanced in THC and CBD content.
- Measurement methods: because of the diversity of hybrid varieties, both gas chromatography (GC) and HPLC are often used to analyze them. GC is useful for quick measurements, while HPLC can provide more detailed information on all cannabinoids present, including THCA and CBDA.
- Dependence on genetics: the THC and CBD content of hybrid varieties depends on their genetic makeup. Hybrids can be both sativa and indica dominant, which determines their cannabinoid profile and associated effects.
Autoflowering varieties
Autoflowering cannabis varieties are unique in that they start blooming based on age rather than the light cycle. These varieties tend to mature faster and are smaller in size.
- Percentage cannabinoid content: autoflowering varieties can contain both high and low levels of THC and CBD, making them versatile for different applications. Some autoflowering varieties are developed for medical purposes and have higher CBD content.
- Measurement methods: HPLC is often used for autoflowering varieties as it allows for accurate measurement of all cannabinoids, including their acidic forms. This is especially important as some autoflowering varieties are used to produce extracts where accurate cannabinoid content is critical.
- Advantages and disadvantages: the main advantage of autoflowering varieties is their ability to mature quickly, allowing for multiple harvests per year. However, due to their smaller size and rapid life cycle, cannabinoid measurement can be less predictable, especially if grooving conditions are not optimal.
Feminized varieties
Feminized cannabis varieties are specifically grown to ensure that all plants are female, which increases flower production and thus cannabinoid production.
- Percentage cannabinoid content: like other types of cannabis, feminized varieties can vary in THC and CBD content depending on genetics and grovelling conditions. Feminized varieties tend to have high THC content, making them popular among recreational users.
- Measurement methods: HPLC is the preferred method for measuring cannabinoids in feminized varieties because it allows for accurate measurement of both THC and CBD content. This is especially important for growers looking to maximize efficiency and crop quality.

WARNING! Errors Seeds does not encourage or encourage you to grow cannabis. Cultivation is prohibited by the legislation of Ukraine. The article is only of scientific and educational interest.








Write a comment